Vibrating wire embedded strain gauge
div, ul, li, a{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul, li { list-style: none; } a { text-de
Vibrating wire embedded strain gauges are mainly used for strain monitoring of various structures such as bridges, tunnels, dams, and pile foundations. They have high accuracy, resolution and good stability . Buried in concrete structures, or bundled on steel bars, it is used for strain measurement of structures. The built-in temperature sensor can simultaneously measure the temperature of the layout point for the temperature correction of the embedded strain gauge, and the matching components can be added as required to form a multi-directional strain gauge group and a stress-free gauge. The embedded strain gage uses a four-core cable.
This product is widely used in strain monitoring in various structural safety monitoring projects such as bridges, tunnels, dams, and pile foundations.
working principle:
When the internal stress of the measured structure changes, the strain gauge senses the deformation synchronously, and the deformation is transmitted to the vibrating wire through the front and rear seats and transformed into the change of the vibrating wire stress, thereby changing the vibration frequency of the vibrating wire. The electromagnetic coil excites the vibrating wire and measures its vibration frequency. The frequency signal is transmitted to the reading device through the cable, and the strain inside the measured structure can be measured. Simultaneously measure the temperature value of the buried point.
Application areas:
Гҳ Stress and strain monitoring of key sections of bridges
Гҳ stress and strain monitoring of concrete dams in dams
Гҳ monitoring of lining in tunnel
Гҳ Stress monitoring of concrete supports in foundation pit support structures
Гҳ Stress and strain monitoring of cast-in-place piles in pile foundations
Гҳ Other civil engineering structure safety monitoring
Product related parameters:
model | SCI-YBJ-NM -XX ( XX represents different ranges) |
Standard range | Вұ 1500ОјОө , Вұ 2500ОјОө , Вұ 3000ОјОө |
Sensitivity | 1 ОјОө _ |
precision | 1%FS |
range of working temperature | -20 в„ғ ~80 в„ғ |
signal type | vibrating wire signal |
Is there temperature compensation | Have |
gauge length | 150mm |
Package | cable etc. |
The structure diagram of the instrument is as follows:
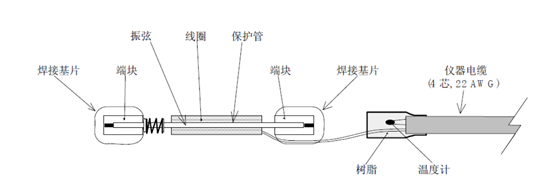
The installation method is as follows:
1. According to the requirements of the design drawings, find the points to be monitored, and bind the strain gauges to the steel bars or steel cables with tie wires. Be careful not to bind them too tightly to ensure that the strain gauges are not stretched or compressed in the longitudinal direction, otherwise it will cause If the measurement is inaccurate or the strain gage may be damaged when concrete is poured, a flexible material (such as sponge, etc.) should be added between the embedded strain gage and the steel bar to avoid vibration damage to the strain gage during concrete pouring and vibrating.
2. After the binding is completed, care must be taken to avoid damage to the strain gauge and transmission cable due to vibration during the process of pouring concrete. It is recommended not to vibrate with a mechanical vibrator in a certain area where the sensor is installed, it is better to use a manual vibrator. It should also be noted that the installation position of the strain gages during the concrete pouring process cannot be greatly shifted due to vibration, otherwise the measured data may be inaccurate.
3. Use a portable collector for data collection and read the installed pre-reading. Make sure there are no problems with installing the lashings and pouring the concrete. Record the location of the buried point and the number of the corresponding strain gauge installed.
4. Connection of epitaxial data transmission lines. The transmission line of the embedded strain gauge is connected . It is recommended to use an electric soldering iron and solder to weld the joints together. Then, use heat shrink tubing to protect the joints, plus waterproof tape and insulating tape. The joints should be waterproof and leak-proof. When laying the transmission line, the transmission line can be walked along the steel bar or steel cable, and the transmission line can be tied to the steel bar or steel cable with nylon cable ties at certain distances. Note that the binding must not be too tight, and the cable routing should also maintain a certain amount of slack, otherwise the cable may be damaged when pouring concrete. It is recommended to use plastic hoses to protect the cables.